Distinguish between organic and inorganic compounds
Organic compounds are compounds that contain carbon found in living organisms.
There are exceptions, which include
carbon dioxide, hydrogen carbonates (product of carbon dioxide and water) and
calcium carbonate.
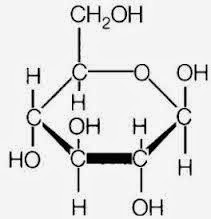
Ribose structure
(Rosalind.info)
Fatty
Acids structure (courses.washington.edu)
Three examples each of monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides
Monosaccharides: glucose, galactose, fructose.
Disaccharides: maltose, lactose, sucrose.
Polysaccharides: starch, glycogen,
cellulose.
One function of glucose, lactose and glycogen in animals, and of fructose, sucrose and cellulose in plants
Glucose: carried by blood to transport
energy to cells throughout the body.
Lactose: sugar in milk, provides energy
to young animals until they are weaned.
Glycogen: short term energy storage in
liver and in muscles.
Fructose: used to make fruits sweet
tasting, attracting animals to disperse seed in fruit.
Sucrose: carried by phloem to transport
energy to cells throughout plant.
Cellulose: used to make strong fibres
that are used to construct the plant cell wall.
Role of condensation and hydrolysis in relationships
Condensation reactions - molecules joined
and water is byproduct.
Hydrolysis reactions - requires water to
break covalent bond between 2 subunits.
Polypeptides
+ water = dipeptide or amino acids.
Glycerides (or triglycerides)
+ water = fatty acids + glycerol.
Three functions of lipids
Lipid functions: energy storage, thermal insulation, buoyancy.
Lipid functions: energy storage, thermal insulation, buoyancy.
Compare the use of carbohydrates and lipids in energy storage
Lipids: more energy per gram than
carbohydrates - stores of lipids are lighter than those of carbohydrates.
Lipids: insoluble in water, do not cause
problems with osmosis in cells.
Carbohydrates: more easily digested than
lipids so energy stored in them can be released easily.
Carbohydrates: soluble in water so are
easier to transport to and from store.



No comments:
Post a Comment